Glossary of Terms
Enter
a term in the text box and press Find.
For a list of terms, select a letter or enter starting letter(s). |
|
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
M
N
O
P
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
[All]
|
|
|
- C-11 PIB
- Carbon-11-labeled Pittsburgh Compound B, (C-11 PIB), is a radiotracer used with positron emission tomography (PET) scanning to image the build-up of beta-amyloid plaques in the brain, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
- calcification
- The process by which noncellular material in the body becomes hardened due to deposits of calcium and other materials.
- calcium score
- A number reflecting the degree and extent of calcium deposits in the walls of the coronary arteries, as demonstrated by cardiac computed tomography.
- cancer
- (kan-ser)
- General term frequently used to indicate any of various types of malignant neoplasms, most of which invade surrounding tissues, may metastasize to several sites, and are likely to recur after attempted removal and to cause death of the patient unless adequately treated.
- carcinoembryonic antigen
- A protein normally found in the tissue of developing babies, but can also be produced by certain types of cancers in adults.
- cardiac catheterization
- A diagnostic procedure in which a catheter is placed in a large vein in the leg or arm and advanced to the heart to check for blood pressure within the heart, oxygen in the blood, and/or pumping ability of the heart muscle. (Also see angiography and angioplasty.)
- cardiac pacemaker
- An electrical device, often implanted, that maintains a normal heart rhythm by stimulating the heart muscle.
- cardiologist
- A physician specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of heart disease.
- C-arm
- An x-ray image intensifier.
- carotid artery
- (ka-rot-id ar-ter-E)
- One of the two major arteries running through either side of the neck, which supply blood to the brain.
- carotid endarterectomy
- A surgical procedure in which plaque buildup is removed from the carotid arteries.
- CAT scan
- See computed tomography (CT).
- cathartic
- A substance that causes evacuation of the bowel.
- catheter
- (kath-i-ter)
- A tubular instrument to allow passage of fluid from or into a body cavity.
- Especially a catheter designed to be passed through the urethra into the bladder to drain it of retained urine.
- A flexible, hollow plastic or rubber tube that may be passed into a blood vessel to withdraw fluids or inject medicine or contrast materials.
Click images to view larger
More images
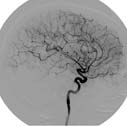
- catheter angiography
- An examination of blood vessels by injecting contrast material directly into an artery through a small plastic tube.
For details see the Catheter Angiography page.
- catheter-directed thrombolysis
- A procedure in which a catheter is inserted through the skin into a vessel and directed to a blood clot in a fistula or graft of a hemodialysis patient. A medication or mechanical device delivered via the catheter is used to break up the clot and restore blood flow. See the Catheter-directed Thrombolysis page for more details.
- cauterize
- To use heat, usually from radiofrequency energy or a laser, to destroy tissue or seal blood vessels.
- CEA assay
- A test that measures the level of a protein called carcinoembryonic antigen in the blood, which is often elevated in cases of cancer.
- cecum
- A saclike pouch connecting to the point where the small and large intestines join.
- celiac disease
Also known as gluten intolerance.
A condition in which sensitivity to gluten (a protein found in wheat, barley and rye) may cause pain, diarrhea, inflammation and damage to the small intestine, and inability to absorb certain vitamins.
- cephalometric
- The measurement of the head.
- cerebral
- Relating to the brain.
- cerebral embolism
- See embolic stroke.
- cerebrospinal fluid
- Fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord and helps to cushion and protect them.
- cervical
- Refers to the neck region of the spinal column which includes seven bones, or vertebrae, labeled C-1 through C-7. It can also refer to the cervix as it relates to cervical cancer.
- cervix
- The lower part of the uterus, connecting the uterus with the vagina.
- chemotherapy
- (kEm-O-ther-a-pE)
- Treatment of disease by means of chemical substances or drugs; usually used in reference to neoplastic (cancer) disease.
- Chiari malformation
- A condition in which brain tissue involving the part of the brain called the cerebellum protrudes into the spinal canal.
- cholecystitis
- An inflammation of the gallbladder that causes abdominal pain. For additional information see the Cholecystitis page.
- cholesterol
- A compound found in most body tissues and an important component of cell membranes. High concentrations in the blood, derived mainly from animal fats in the diet, are thought to promote atherosclerosis.
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- A general term for chronic diseases such as bronchitis and emphysema that cause the airways in the lung to become narrowed, limiting airflow to and from the lungs and causing shortness of breath. For more information see the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) page.
- claudication
- Pain, fatigue and cramping in the legs brought on by walking that goes away when at rest.
- claustrophobic
- (klaw-strO-fO-bik)
- A morbid fear of being in a confined place.
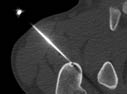
- clopidogrel
- Also called Plavix®
One of a class of medications called antiplatelet drugs that help prevent harmful blood clots that may cause heart attacks or strokes.
Click images to view larger
More images
- closed bone biopsy
- Also called needle bone biopsy.
An image-guided procedure in which a needle is used to remove a small sample of bone from the body to be examined under a microscope.
- clot
- To coagulate or turn from a free-flowing liquid to a thickened or semi-solid state.
- clubbing
- An enlargement of the fingertips, which may occur as a result of advanced diffuse interstitial lung disease.
- cluster headache
- Headaches that occur in groups, or clusters, over a period of several weeks or months separated by headache-free periods of months or years. Cluster headaches include sharp, penetrating pain around or behind one eye, watering of the eye and a stuffy nose.
- coagulate
- To change from a liquid to a thickened or solid state. Blood that does not flow smoothly through a vessel can coagulate or clot by turning from a free-flowing liquid to a semi-solid gel.
- cobalt (Co)
- (kO-bawlt)
- A steel-gray metallic element, atomic no. 27, atomic wt. 58.93320; a bioelement and a constituent of vitamin B12; certain of its compounds are pigments, e.g., cobalt blue.
- cobalt-60 radiation therapy
- Cobalt-60-based or photon radiation therapy machines are used exclusively to treat brain tumors and abnormalities. See also Gamma Knife.
- collodion
- A liquid that, on evaporation, leaves a protective film over cuts.
- colon
- Part of the body’s digestive tract and a component of the digestive system, a complex process that enables the body to break down and absorb food and eliminate waste. The colon is comprised roughly of the first five or six feet of the large intestine.
- colonoscope
- A long flexible tube with a tiny camera at the end used in a procedure called a colonoscopy, which captures images of the interior of the colon and rectum.
- colonoscopy
- (kO-lon-os-ko-pE)
- Visual examination of the inner surface of the colon by means of a lighted, flexible tubular instrument inserted into the colon through the rectum.
Click image to view larger
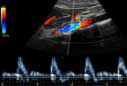
- color Doppler
- Color Doppler uses a computer to convert the Doppler measurements into an array of colors. This color visualization is combined with a standard ultrasound picture of a blood vessel to show the speed and direction of blood flow through the vessel.
- colorectal cancer
- Colorectal cancer is cancer that forms in the large intestine (colon or rectum), in the lower part of the body’s digestive tract, a long twisting tube that extends from the mouth to the anus. This tract is part of the digestive system, a complex process that enables the body to break down and absorb food and eliminate waste.
For more information see the Colorectal Cancer Treatment and Colorectal Cancer Screening pages.
- colostomy
- Establishment of an artificial opening into the colon.
- coma
- A state of deep unconsciousness that lasts for a prolonged or indefinite period, caused by severe injury or illness.
Click images to view larger
More images
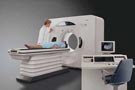
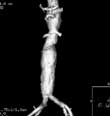
- computed tomography (CT)
- (tO-mog-ru-fE)
- Sometimes referred to as CAT scan (computerized axial tomography).
Imaging anatomical information from a cross-sectional plane of the body, each image generated by a computer synthesis of x-ray transmission data obtained in many different directions in a given plane.
Developed in 1967 by British electronics engineer Godfrey Hounsfield, CT has revolutionized diagnostic medicine. Hounsfield linked x-ray sensors to a computer and worked out a mathematical technique called algebraic reconstruction for assembling images from transmission data. In 1973, the Mayo Clinic began operating the first machine in the U.S. Early machines yielded digital images with at least 100 times the clarity of normal x-rays. Subsequently, the speed and accuracy of machines has improved many times over. CT scans reveal both bone and soft tissues, including organs, muscles, and tumors. Image tones can be adjusted to highlight tissues of similar density, and, through graphics software, the data from multiple cross-sections can be assembled into 3-D images. CT aids diagnosis and surgery or other treatment, including radiation therapy, in which effective dosage is highly dependent on the precise density, size, and location of a tumor.
Click images to view larger
More images
- computed tomography (CT) angiography
- ( tO-mog-ru-fE an-jE-O-gra-fE)
- A method of examining blood vessels utilizing x-rays and injection of iodine-rich contrast material (dye).
For details see the CT Angiography page.
- concussion
- Also known as mild traumatic brain injury.
An injury to the brain that occurs when the head or body is struck hard enough that the brain bounces against the skull.
- conformal radiation therapy
- Use of a CT image to tailor the radiotherapy beam to the exact size and shape of a tumor.
- congenital
- Existing at birth.
- congenital heart disease
- A heart problem that has existed since birth.
- congestive heart failure
- A condition in which the heart cannot adequately pump blood forward, leading to a back-up of blood in vessels and an accumulation of fluid in body tissues including the lungs.
- constipation
- (kon-sti-pA-shun)
- A condition in which bowel movements are infrequent or incomplete.
- contrast agent
- See contrast material.
- contrast material
- Also referred to as contrast agent or contrast medium. Any internally administered substance that has a different opacity from soft tissue on radiography or computed tomography. Includes:
- Barium or water, used to make parts of the
gastrointestinal tract opaque.
- Iodine in water, used for arthrography.
- Water soluble iodine, used to make blood vessels opaque; to demonstrate the inner structures of the urinary tract (kidneys, ureters and bladder); and to outline joints (the spaces between two bones).
- Iodine mixed with water or oil may be used to evaluate the fallopian tubes and lining of the uterus.
- Sterile saline (salt water) is used during hysterosonography.
- May refer to air occurring naturally or introduced into the body.
- Paramagnetic substances used in magnetic
resonance imaging.
For more imformation pleasse refer to the Contrast Materials page.
- contrast medium
- See contrast material.
- contusion
- A bruise resulting from trauma in which blood seeps into surrounding tissue.
- core needle biopsy
- A type of biopsy in which a large hollow needle is inserted through the skin to the site of an abnormal growth to collect and remove a sample of cells for analysis. This procedure uses an automated needle, which obtains one sample of tissue at a time and is re-inserted several times.
- coronary arteries
- (kOr-o-nAr-E ar-ter-Es)
- The arteries that supply freshly oxygenated blood to the heart muscle.
- coronary artery bypass graft surgery
- This surgery increases blood flow to the heart by using a vein, or an artery from elsewhere in the body, and using it to divert blood around the area of narrowing or blockage in the coronary arteries of the heart.
Click image to view larger

- coronary artery disease
- A condition involving the narrowing of the coronary arteries that carry blood and oxygen to the heart muscle.
- coronary bypass surgery
- A surgical means of rerouting blood in the coronary artery system around diseased vessels.
- Coumadin®
- A brand name for warfarin.
- Cowden syndrome
- A disorder characterized by non-cancerous, tumor-like growths and an increased risk of developing certain cancers.
- cranial
- Related to the bony skull known as the cranium that holds the brain.
- craniofacial
- Relating to the face and the cranium (skull that protects the brain).
Click image to view larger
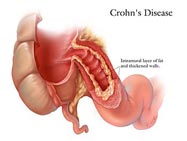
- Crohn's disease (also known as regional enteritis)
- A moderately severe chronic inflammation of the intestine, especially of the small intestine, of unknown cause, involving the obstruction of the lower part of the small bowel and less frequently other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. It is characterized by patchy deep ulcers that may cause abnormal passages within the bowel, and narrowing and thickening of the bowel. Symptoms include fever, diarrhea, cramping abdominal pain, and weight loss.
- cryoablation
- See cryosurgery.
Click image to view larger

- cryoprobe
- An instrument used to apply extreme cold to a selected anatomic area.
- cryosurgery
- Also known as cryotherapy, cryoablation or targeted cryoablation therapy.
A minimally invasive treatment that uses extreme cold in the form of liquid nitrogen or argon gas to freeze and destroy diseased tissue, including cancer cells. See the Cryotherapy page for more information.
- cryotherapy
- See cryosurgery.
- CT colonography (CTC)
- Also called virtual colonoscopy.
A procedure in which computed tomography (CT) scanning is used to produce detailed pictures of the inside of the colon and rectum.
- CT enteroclysis
- CT enteroclysis is a special type of computed tomography (CT) imaging that produces detailed images of the small bowel by infusing contrast material through a tube positioned in the upper small bowel.
- CT enterography
- CT enterography is a special type of computed tomography (CT) imaging performed with contrast material to produce images of the small intestine. See the CT Enterography page for more information.
- curettage
- See dilation and curettage (D&C).
- curie (C, c, Ci)
- (kyu-rE)
- A unit of measurement of radioactivity, 3.70 ×1010 disintegrations per second; formerly defined as the radioactivity of the amount of radon in equilibrium with 1 gm. of radium; superseded by the S.I. unit, the becquerel (1 disintegration per second).
Origin
[Marie (1867-1934) and Pierre (1859-1906) Curie, French chemists and physicists and Nobel laureates]
- cyanosis
- A blue coloration in the lips, skin and fingernails as a result of reduced oxygen levels in the blood.
Click image to view larger

- cyclotron
- A type of particle accelerator in which charged particles are propelled by an alternating electric field between two large electrodes in a constant magnetic field created by two large magnets. The particles are injected at the center of the magnet and spiral outward as their energy increases. Protons produced in a cyclotron can be used to treat cancer, and cyclotron-produced protons can create radioisotopes for nuclear medical procedures.
- cystic fibrosis
- An inherited disease in which the lungs, intestines and pancreas become clogged with thick mucus, interfering with normal digestion and breathing.
- cystography
- (sis-tog-ru-fE)
- Radiography of the bladder, following injection of a radiopaque substance. For more information, see the Voiding Cystourethrogram page.
- cystoscopy
- This procedure uses a special camera at the end of a tube that allows the doctor to see inside the bladder.
- cysts
- (sists)
- Abnormal sacs containing gas, fluid, or a semisolid material, with a membranous lining.
|
|