Glossary of Terms
Enter
a term in the text box and press Find.
For a list of terms, select a letter or enter starting letter(s). |
|
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
M
N
O
P
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
[All]
|
|
|
- sacroiliac joint
- joint in the pelvis between the sacrum and the ilium of the pelvis
- saline
- Salt water.
- sarcoma
- A malignant or cancerous tumor that occurs in the connective tissues of the body, including the bones, cartilage, tendons and soft tissues.
- scan(s)
- To survey by traversing with an active or passive sensing device.
- The image, record, or data obtained by scanning, usually identified by the technology or device employed; e.g., CT scan, radionuclide scan, ultrasound scan.
- Abbreviated form of scintiscan (scintigram), usually identified by the organ or structure examined; e.g., brain scan, bone scan.
- sciatica
- Painful inflammation of the sciatic nerve that sometimes results from a herniated intervertebral disc in the spine.
- scintigraphy
- (sin-tig-ru-fE)
- A diagnostic procedure consisting of the administration of a radionuclide that accumulates in the organ or tissue of interest, followed by recording the distribution of the radioactivity with a stationary or scanning external scintillation camera.
- sclerosing
- Causing scarring. Liquid chemicals or alcohols used to destroy blood vessels in an embolization procedure. Sclerosing damages the inner lining of a vessel and causes blood clots (a thickened mass of blood) to form, thus preventing blood flow through the vessel.
- sclerosing cholangitis
- Inflammation of the bile ducts.
- sclerotherapy
- Treatment involving the injection of a sclerosing (hardening) solution into vessels or tissues.
- scoliosis
- A side-to-side curvature of the spine that usually develops in childhood or adolescence.
- screening mammography
- Imaging examination of the breast by means of x-rays, of individuals usually without symptoms, to detect unsuspected breast cancer.
- scrotum
- A muscular sac that contains the testes.
- secondary headache
- One of the two major types of headaches. Secondary headaches are caused by an injury or underlying illness, such as bleeding in the brain, an infection or a brain tumor.
- secure sockets layer (SSL)
- A cryptographic communications protocol that provides secure transmissions on the Internet by encoding/decoding the data transfers.
- sedation, deep
- A level of sedation in which patients will generally sleep during the procedure without responding to painful stimulation. Patients will be able to breathe on their own and in many cases will receive oxygen from a face mask. See sedation, minimal and moderate.
- sedation, minimal and moderate
- Levels of sedation in which the patient receives a drug to relax but remains responsive to verbal questions and painful stimulation. Patient is able to breathe independently during a surgical or medical procedure. See sedation, deep.
- sedation, non-pharmacological
- Approaches that guide a patient to a state of relaxation by focusing attention on pleasant thoughts. Guidance is provided by specially trained radiology or other medical personnel. This condition may be achieved via distraction techniques or self-hypnotic relaxation.
- sedative
- A drug that allows you to relax during a procedure like angiography, often without putting you to sleep.
- seed implantation
- See permanent brachytherapy.
- seizure
- A sudden, uncontrollable wave of electrical activity in the brain that causes involuntary bodily movement, a change in attention or a loss of consciousness.
- seizure disorders
- A condition marked by sudden, uncontrollable waves of electrical activity in the brain, causing involuntary movement or loss of consciousness.
- semen
- (sE-men)
- A thick white fluid, made and stored in male testicles, that carries sperm out of the body through the penis during ejaculation.
- sentinel lymph node
- The first lymph node in a lymph node bed to receive drainage from a tumor site.
- serial paracentesis
- A minimally invasive procedure in which excess fluids in the abdomen are repeatedly withdrawn, either through a needle inserted directly into the peritoneal cavity or through a catheter connected to a peritoneal port, a small reservoir or chamber surgically implanted under the skin near the abdomen.
- sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
- Any infectious disease that is passed from one person to another during sexual contact.
- shear injury
- Also known as diffuse axonal injury.
Stretched or torn nerve fibers in the brain.
- sheath
- A short, hollow plastic tube inserted through the skin into a blood vessel or tissue through which other instruments, such as a guide wire and balloon-tipped catheter are advanced.
- short-bore MRI system
- A type of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) unit. The traditional MRI unit is a large doughnut-shaped magnet with a tube-like central opening. The patient lies on a moveable examination table that slides into the center of the magnet. While the body part that is being scanned must remain in the magnet, the short-bore nature of the magnet allows the part of the body not being scanned to potentially be "outside" of the magnet. Patients often report the short-bore MRI system produces less claustrophobia than a traditional MRI unit.
- sickle-cell anemia
- A severe, chronic type of anemia caused by an abnormal form of hemoglobin that distorts the red blood cells. These abnormal red blood cells sometimes plug the blood vessels, causing damage to the organ downstream.
- sigmoidoscope
- A thin flexible tube with a tiny camera at the end used in a procedure called a sigmoidoscopy, which captures images of the interior of the lower large intestine and rectum.
- sigmoidoscopy
- An examination in which a flexible tube with a tiny camera at the end called a sigmoidoscope is inserted into the colon to capture images of the interior of the lower colon and rectum.
- simulation
- Use of a radiographic system or computer to plan radiation therapy. See also treatment planning.
- single-photon emission-computed tomography (SPECT)
- An imaging test that uses a gamma camera and a computer to create three-dimensional (3-D) images of the distribution of a radiotracer in the body. SPECT is used to study blood flow through the heart muscle, and to study the brain, bones and to detect infection and certain types of tumors.
- sinus (sinuses)
- Hollow, air-filled spaces located within the bones of the face surrounding the nasal cavity. There are four pairs of cavities, called paranasal sinuses, each of which is connected to the nose by small openings.
- sinusitis
- Infection or inflammation of one or more of the sinuses.
- sloughing
- The process in which dead tissue becomes separated from living anatomic structures.
- small intestine
- The section of the gastrointestinal tract that digests food and absorbs nutrients after they have passed through the stomach.
- SmartCards
- A device similar to a credit card that contains electronic information or tokens that identify and validate a user in conjunction with biometric or password information.
- social workers
- Social workers may be available to provide practical help and counseling to patients or members of their families and can help them to cope. They also may help arrange for home health care and other services. Social workers may be licensed. Licensed social workers must have a master's degree and must pass an examination.
- sonographer
- (so-nog-ru-fer)
- An allied health professional who has been specifically trained to perform ultrasound examinations. Many sonographers are certified by a registry of sonographers, provided they meet strict training requirements and pass examinations in basic ultrasound science and clinical applications.
- sonography
- (so-nog-ru-fE)
- Syn: ultrasonography.
The imaging of body structures by measuring the reflection or transmission of high frequency sound waves. Computer calculation of the distance to the sound-reflecting or -absorbing surface plus the known orientation of the sound beam gives a two- or three-dimensional image.
- sonohysterography
- Sonography of the uterus and fallopian tubes using a transvaginal probe following the injection of sterile saline into the uterus via a thin catheter inserted through the cervix.
- spectral Doppler
- Instead of displaying Doppler measurements visually as in the color and power Doppler methods, spectral Doppler displays the blood flow measurements graphically, displaying flow velocities recorded over time.
- speculum
- (spek-yU-lum)
- An instrument for enlarging the opening of a canal or cavity in order to facilitate inspection of its interior.
- sperm
- Sperm (or spermatozoa) is the male reproductive cell carried by semen through the penis when a man ejaculates.
- sphincterotomy
- A procedure in which a small incision is made in the opening of the bile duct to allow bile and small gallstones to drain.
- spinal anesthesia
- Administration of a local anesthetic into the subarachnoid space surrounding the spinal cord. Generally used to prevent pain and movement in areas below the chest and extending to the feet.
- spinal canal
- The cavity within the vertebral column through which the spinal cord passes.
- spinal cord
- A cylindrical bundle of nerves, lying within the vertebral column, that carries sensory messages from peripheral nerves to the brain, and motor impulses from the brain to the body's muscles.
- spinal fusion
- Surgical fixation of an unstable segment of the spine.
- spirometer
- A device that measures the volume of air that moves in and out of the lungs.
- spirometry
- A test of lung function using a spirometer, a device that measures the volume of air that moves in and out of the lungs.
- spleen
- (splEn)
- A large vascular lymphatic organ lying in the upper part of the abdominal cavity on the left side, beside the stomach and below the diaphragm. It is a blood-forming organ in early life and later a storage organ for red corpuscles and platelets; because of the large number of macrophages, it also acts as a blood filter.
- splenoportography
- (sple-nO-pOr-tog-ru-fE)
- Introduction of radiopaque material into the spleen to obtain an x-ray visualization of the portal vessel of the portal circulation.
- spontaneous pneumothorax
- A condition in which a collection of air in the pleural space causes the lung to collapse, occurs in the absence of disease or injury.
- spot films
- X-rays of a localized region, usually under study by fluoroscopy.
- sputum
- A mixture of saliva and mucus coughed up from the respiratory tract.
- sputum cytology
- A diagnostic test in which a sample of sputum (mucus) is examined under a microscope to determine whether abnormal cells are present.
- stage
- Extent or progression of a disease such as cancer.
- staging
- Determining the extent or progression of a disease such as cancer.
Click image to view larger
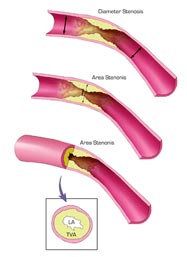
- stenosis, pl. stenoses
- (sten-O-sis, sten-O-sEs)
- An abnormal narrowing of any canal; for example, a narrowing of one of the cardiac valves.
- Narrowing of an opening or passageway in the body. Stenosis of an artery may reduce blood flow through the vessel.
- stent
- Slender thread, rod, or catheter, lying within the space in the interior of a tubular structure, such as an artery or the intestine. Used to provide support during or after opening surgically, or to assure the opening of an intact but contracted lumen.
- stent graft
- A synthetic tube-like device used to replace a portion of an artery that has weakened and bulged (called an aneurysm).
- stenting
- The act of placing a stent.
- stereotactic biopsy
- An x-ray procedure that uses multiple coordinates to precisely determine the location of a tumor or nodule so that a tissue sample may be obtained.
- stereotactic radiosurgery
- A highly precise form of radiation therapy that directs narrow beams of radiation from different angles at a brain tumor or abnormality. Using a device that keeps the head completely still, this treatment minimizes the amount of radiation to healthy brain tissue. For more information see the Stereotactic Radiosurgery page. See also stereotactic radiotherapy.
- stereotactic radiotherapy
- A form of stereotactic radiosurgery using fractionated radiation dose (smaller dose over a period of days or weeks) or hyperfractioned dose (smaller dose two to three times a day), as opposed to a single large dose, to minimize tissue damage. Also see stereotactic radiosurgery.
- sternum
- The breastbone (the long, flat bone that forms the front of the chest cage).
- stones
- See: Gallstones or Kidney and Bladder Stones.
- stress echocardiography
- A test in which ultrasound is used to create moving pictures of the heart before and after the heart is stressed either through exercise or a medication that stimulates the heart.
- stress test
- A heart monitoring test to discover how well the heart works, usually performed via physical exercise, sometimes via drugs to simulate heart stress.
- stroke
- A stroke occurs when a blood vessel that carries oxygen and nutrients to the brain is either blocked by a clot or bursts, interrupting blood flow to an area of the brain. When either of these happens, brain cells begin to die and brain damage occurs. See the Stroke page for more information.
- subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Blood collection between middle (arachnoid) and inner (pia mater) linings of the brain. It can be a result of trauma, or a bursting (ruptured) aneurysm. An aneurysm is a small area of weakness of the wall of an artery, which may be congenital, or less commonly, due to other causes, such as an infection.
- subarachnoid space
- The space between the membrane covering the spinal cord and the cord itself.
- subclavian vein
- A major vein running under the collarbone (clavicle) which receives blood from the large vein of the upper arm and returns toward the heart.
- subcutaneous port
- A special device used in a vascular access procedure that is inserted inside a major vein for a period of months or years so that blood can be repeatedly drawn or medication and nutrients can be injected into the patient’s bloodstream on regular basis. The subcutaneous implantable port is a permanent device that consists of a catheter, a long, thin, hollow plastic tube, attached to a small reservoir, both of which are placed under the skin.
- subdural hematoma
- In this type of hematoma, a blood vessel (usually a vein) bursts in a space just outside of the brain. Blood begins to pool along the surface of the brain, between membranes that cover the brain. Because subdural hematomas arise from low pressure venous bleeding, it may take some time for symptoms to appear after the injury. By contrast, an epidural hematoma, which is blood bleeding between the skull and a tough membrane normally firmly attached to the skull, called the dura mater, usually arises from an artery torn by a skull fracture. The higher pressure arterial blood accumulates much more quickly, usually resulting in a rapid appearance of symptoms (e.g., headache, paralysis, disturbance of consciousness).
- superior vena cava
- One of the largest veins in the body, it returns blood from the entire upper half of the body directly to the right atrium, one of the heart chambers.
- surgical shunt
- A surgically created passageway to allow blood or other bodily fluids to flow between two locations. A shunt may be used to move fluid from one part of the body to another or to divert blood flow from one route to another.
- sutures
- Stitches used to hold tissue together or to close a wound.
- synchrotron
- A cyclic particle accelerator in which the magnetic field (to turn the particles so they circulate) and the electric field (to accelerate the particles) are synchronized with the traveling particle beam. While the cyclotron uses a constant magnetic field and a constant frequency electric field, both are varied in the synchrotron. This allows for construction of large rings that can accelerate particles to much higher energies than a cyclotron which has a limited magnet size. The synchrotron uses multiple separate bending magnets and narrow bore tubes to connect them. It can be used to produce high energy protons and other particles such as carbon ions that are used to treat cancer. In addition the energy of the particles can be varied as needed which is very difficult in a cyclotron.
- syphilis
- A venereal disease that can cause lesions of the central nervous and cardiovascular systems.
|
|