Glossary of Terms
Enter
a term in the text box and press Find.
For a list of terms, select a letter or enter starting letter(s). |
|
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
M
N
O
P
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
[All]
|
|
|
- pacemaker
- See cardiac pacemaker.
- pack-years
- A measure of an individual’s cigarette smoking history equal to the number of cigarette packs smoked per day multiplied by the number of years the individual has smoked.
- palliative treatment
- Treatment designed to relieve or control symptoms rather than to cure disease.
- palpable
- Able to be felt; perceptible to touch
- Evident; plain
- pancreas
- (pan-krE-us)
- A gland that produces several hormones and secretes digestive enzymes, or proteins that act as a catalyst for the breakdown of food, through the pancreatic duct that connects the gland to the intestine. The pancreas also secretes hormones, most importantly insulin, into the blood to regulate metabolism of the body.
- pancreatic duct
- A tubular passageway that connects the pancreas to the intestine.
- pancreatitis
- Inflammation of the pancreas.
- pancreatography
- (pan-krE-a-tog-ru-fE)
- Radiographic demonstration of the pancreatic ducts, after injection of radiopaque material into the distal duct.
- Pap test
- Microscopic examination of cells scraped from a mucosal surface, then stained. Used especially for detection of cancer of the uterine cervix.
- papilloma
- A non-cancerous tumor of the milk duct.
- paracentesis
- A minimally invasive procedure in which a thin needle or tube is inserted into the abdomen to remove excess fluid from the peritoneal cavity.
- paranasal
- (par-a-nA-sul)
- Alongside the nose.
Click image to view larger
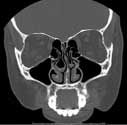
- paranasal sinuses
- Hollow, air-filled spaces located within the bones of the face surrounding the nasal cavity. There are four pairs of cavities, called paranasal sinuses, each of which is connected to the nose by small openings.
- parathyroid glands
- Typically four small raisin-sized glands in the neck primarily involved in the regulation of calcium and phosphorus levels in the body.
- parathyroid imaging
- Evaluation of the parathyroid glands, accomplished with a nuclear medicine technique using a material called Sestamibi, or the parathyroid glands can be imaged with ultrasound, CT or MRI.
- partial bowel resection
- See partial colectomy.
- partial colectomy
- Removal of part of the colon.
- particle beam radiation therapy
- Particle or proton beam radiation therapy is a type of radiation therapy that uses protons as the source of radiation rather than x-rays. Protons can pass through healthy tissue without damaging it. See the Proton Therapy page for more information.
- particulate agents
- Synthetic materials that are suspended in liquid and injected into a blood vessel to form a permanent barrier to blood flow. They are used in embolization procedures to stop bleeding or block arteries that provide blood flow to a tumor.
- patency
- (pA-ten-sE)
- The state of being freely open or exposed.
- pathologic
- Morbid or diseased; resulting from disease.
- pathologist
- A physician specializing in the examination of cells and tissues.
- pathology
- The study of disease processes.
- penetrating injury
- An injury in which the skin is broken as the result of a cut (laceration).
- percutaneous
- (per-kyU-tA-nE-u)
- A passing through the skin, as in absorption of an ointment containing the active ingredient; also passage through the skin by needle puncture, including introduction of wires and catheters.
- percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC)
- An x-ray procedure that involves the injection of a contrast material directly into the liver to produce pictures of the bile ducts.
- perforation
- A hole in the walls of an organ or structure of the body that develops from a weak spot in the organ or from a deep penetrating wound caused by trauma.
- perfusion
- (per-fyU-zhun)
- The flow of blood or other fluid to an organ.
- pericardial effusion
- (pAr-E-kar-dE-al)
- Excessive fluid within the sac surrounding the heart, usually due to inflammation.
- perineum
- The area between the thighs, extending from the rectal area to the pubic area.
- periodontal disease
- Disease that affects the tissue and bone surrounding the teeth.
- peripheral artery disease (PAD)
- See peripheral vascular disease (PVD).
- peripheral vascular disease (PVD)
- Also called peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Arteriosclerosis in arteries of the arms or legs, which become narrow from the build up of plaque and eventually may cause severe symptoms due to lack of adequate blood flow. The most common form is disease in large vessels supplying the legs, which causes severe pain on walking and may in time make a patient immobile. See the Peripheral Artery Disease page for more information.
- peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC)
- A special type of catheter used in a vascular access procedure that is inserted inside a major vein for a period of weeks, or months so that blood can be repeatedly drawn or medication and nutrients can be injected into the patient’s bloodstream on regular basis. Unlike a standard intravenous catheter (IV) which is for short term use, a vascular access catheter is more durable and does not easily become blocked or infected. The peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) typically provides access for 4-8 weeks but may remain in place for up to six months.
- peritoneal cavity
- Also called abdominal cavity.
The space within the peritoneum not occupied by the abdominal organs. In most circumstances, this space is empty and the cavity is collapsed. In certain disease, this space can become filled with fluid. In other circumstances, this space may be intentionally inflated with carbon dioxide for laparoscopic surgery, or with a sterile solution for peritoneal dialysis.
- peritoneal port
- A small reservoir or chamber about the size of a quarter that is surgically implanted under the skin near the abdomen. The port has a silicone rubber top that can be penetrated by a needle and an attached catheter that is designed to hang down into the abdominal or peritoneal cavity.
- peritoneum
- A membranous sac consisting of a thin layer of connective tissue that lines the abdominal cavity.
- periventricular leukomalacia (PVL)
- Damage to white matter brain tissue as a result of a lack of oxygen or blood flow to the brain prior, during or after birth.
- permanent brachytherapy
- Also called seed implantation.
A radiation therapy treatment for cancer in which radioactive material sealed inside a pellet (a “seed”) is placed and permanently left inside the body in or near a tumor.
- peroxide
- Also known as hydrogen peroxide, a liquid bleaching agent used as a disinfectant.
- petit mal seizure
- Also called an absence seizure.
A type of seizure or convulsion often associated with epilepsy in which the patient stares into space for a short period of time.
- pharyngeal
- Related to the pharynx, or throat.
- pharynx
- Also known as the throat, the passageway that extends from immediately behind the mouth and nasal cavity to the esophagus and stomach.
- phlebectomy
- Excision of a segment of a vein, performed sometimes for the cure of varicose veins.
- phlebitis
- Painful inflammation of the veins.
- photodynamic therapy
- A form of treatment in which a drug is administered and then activated by light.
- photon radiation therapy
- See cobalt-60 radiation therapy.
- physicist
- (fiz-i-sist)
- A specialist in the science of physics.
- Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS)
- A computer system for acquiring, storing, viewing, and managing digital medical imaging studies and related information.
- pituitary gland
- An endocrine gland located beneath the brain that supplies numerous hormones that govern many vital processes in the body.
- plaque
- (plak)
- A build-up of fat and other substances on the inner wall of a blood vessel. In time, plaque may build up and limit blood flow through the vessel.
- platelets
- Particles that are formed in bone marrow and circulate in the blood. They bind at the site of a wound to begin the clotting process.
- platinum coils
- A type of coil, made of soft platinum wire smaller than a strand of hair, used in a procedure called a detachable coil embolization to treat an aneurysm (a bulge) or a blood vessel malformation called a fistula (a false passageway) that occurs in the brain and other parts of the body. Using image guidance, the coils are placed at the site of an aneurysm or fistula, where it helps block the flow of blood or prevents a rupture of the vessel.
- Plavix®
- A brand name for clopidogrel.
- pleural effusion
- An excess of fluid in the pleural cavity, the space that surrounds the lungs and lies underneath the chest wall.
- pleural membrane
- A thin layer of tissue that lines the outside of the lungs and the inside of the chest wall.
- pleural space
- Also called pleural cavity.
The cavity that exists between the lungs and underneath the chest wall. It is normally empty, with the lung immediately against the inside of the chest wall. In some diseases, fluid can build up in this space (a pleural effusion). In trauma, air can enter this space (a pneumothorax). Under either condition, excessive fluid or air in the pleural space can cause difficulty breathing since the lung is prevented from inflating fully.
- pleurisy
- (plur-i-sE)
- Inflammation of the membrame encasing the lungs.
- pneumonia
- (nU-mO-nE-a)
- Inflammation of the lung. Most cases are due to infection by bacteria or viruses, a few to inhalation of chemicals or trauma to the chest wall. See the Pneumonia page for more information.
- pneumothorax
- A condition in which a collection of air in the pleural space causes the lung to collapse, occurs during heart or lung surgery or as a result of a traumatic injury (such as a gunshot or stab wound) to the chest.
- pneumothorax
- A condition in which air escapes from the lungs into the space between the lung and the chest wall. With the loss of the negative pressure of the pleural space, the lungs cannot expand fully.
- polycythemia
- A disorder in which there is an abnormal increase in the number of red blood cells in the blood.
- polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)
- An acrylic cement used to repair bone fractures and in other orthopedic procedures.
- polyp
- A mass that bulges outward from a normal tissue surface, usually appearing as an irregular mound-like structure growing from a broad base or a slender stalk.
- polypectomy
- A procedure using an endoscope in which abnormal growths called polyps are removed from the inner walls of the colon and rectum.
- porous
- Having small holes or pores.
- portal hypertension
- Blockage of normal blood flow through the liver, usually the result of cirrhosis, which can lead to back-pressure on the veins of the portal (intestinal) circulation, variceal bleeding and ascites.
- portal vein
- The main vein that drains blood from the digestive tract to the liver for filtration.
- Port-o-cath
- Manufacturer's name. See implanted port.
- portography
- (pOr-tog-ru-fE)
- Imaging of the portal circulation by x-rays, using contrast material, usually introduced into the spleen or into the portal vein at operation.
Click image to view larger

- positron emission tomography (PET)
- Positron emission tomography, also called PET or a PET scan, is a diagnostic examination that involves the development of biologic images based on the detection of subatomic particles. These particles are emitted from a radioactive substance given to the patient. The subsequent views of the human body are used to evaluate function. For more details see the PET/CT page.
- post-embolization syndrome
- A condition that includes pain, nausea, vomiting and low-grade fever that many patients experience following a chemoembolization procedure in which anticancer drugs are injected directly into a cancerous tumor and a synthetic material is placed inside the blood vessels that supply blood to the tumor to prevent blood from flowing to the area.
- posteroanterior view
- (pos-ter-O-an-tEr-E-or)
- A term typically denoting the direction of x-rays, from posterior to anterior, through a body part.
Click image to view larger
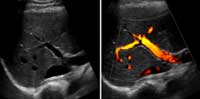
- power Doppler
- An ultrasound technique that is more sensitive in detecting blood flow than color Doppler. Power Doppler is able to obtain images that are difficult or impossible to obtain using standard color Doppler and to provide greater detail of blood flow, especially in vessels that are located inside organs.
Although power Doppler may be more sensitive than color Doppler for detection and demonstration of blood flow, power Doppler provides no information about the direction of flow. Color and spectral Doppler both reveal the direction of blood flow which can be valuable information.
- precancerous
- Abnormal tissue changes that often are found before cancer develops.
- primary headache
- One of the two major types of headaches. Primary headaches, which include cluster, migraine and tension headaches, are not associated with a medical condition or disease.
- primary tumor
- A tumor that originates at its location. See also tumor.
- probe
- (prOb)
- A slender rod of flexible material, with blunt bulbous tip, used for exploring sinuses, fistulas, other cavities, or wounds.
- A device or agent used to detect or explore a substance; e.g., a molecule used to detect the presence of a specific fragment of DNA or RNA or of a specific bacterial colony.
- To enter and explore, as with a probe.
- proctoscopy
- This procedure uses a special camera at the end of a tube that allows the doctor to see inside the rectum.
- prognostic
- Predicting the clinical course of a disease.
- prophylactic cranial radiation
- Exposure of the brain to low-dose radiation in a cancer patient in order to prevent the tumor from spreading to this site.
- prostate cancer
- Abnormal cells that grow into a mass of tissue called a tumor in the prostate gland.
- prostate gland
- (pros-tAt)
- A walnut-size gland in men that surrounds the urethra and the base of the bladder. The prostate, part of the male reproductive system, makes some of the milky fluid called semen that carries sperm.
- prostatitis
- An inflammation of the prostate gland.
- protected health information (PHI)
Any information relating to a patient's physical or mental health, the details of one's care, or the payment for that health care. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) defines all of the following as individually identifiable health information:
- Names and addresses
- Identifying Dates – date of birth, date of admission, date of examination.
- Specific age if over 89 years old.
- Telephone and fax numbers, Social Security numbers, medical record or account numbers, employee numbers, health plan numbers, email addresses, vehicle identifiers, license numbers.
- Full face images or biometric identifiers such as finger and/or voice prints.
- Any unique identification numbers, codes or characteristics that may be traced back to
an individual.
- proton
- A positively charged particle that is a fundamental component of the nucleus of all atoms.
- proton beam radiation therapy
- See particle beam radiation therapy.
- pulmonary
- Related to the lungs or the respiratory system, the complex of organs and structures that exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and blood circulating through the lungs.
- pulmonary edema
- A build-up of fluid in the lungs and a swelling of lung tissue.
- pulmonary embolism
- Blockage of the arteries in the lungs, most frequently by detached fragments of a blood clot from a leg or pelvic vein, commonly when that clot follows an operation or confinement to bed.
- pulmonary hypertension
- A condition of abnormally high blood pressure within the network of blood vessels between the heart and lungs that delivers oxygen to the blood and removes carbon dioxide.
- pulmonologist
- A physician that practices in the medical specialty of pulmonology, which deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract.
- pulse oximetry
- A test that involves a small device placed on a finger tip to measure the oxygen saturation of the blood.
- pyelography
- (pI-a-log-ru-fE)
- Radiologic study of the kidney, ureters, and usually the bladder, performed with the aid of a contrast material either injected intravenously, or directly from below via the urethra, or from above through the kidney (either via a direct puncture or through a previously placed catheter).
- pyelonephritis
- Bacterial infection of the kidney.
- pylorus
- The passage from the stomach into the small intestines.
|
|