Glossary of Terms
Enter
a term in the text box and press Find.
For a list of terms, select a letter or enter starting letter(s). |
|
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
M
N
O
P
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
[All]
|
|
|
- B cell
- A type of lymphocyte or white blood cell that is an essential component of the immune system. Non Hodgkin B cell lymphoma begins in B cells.
- balloon angioplasty
- An image-guided procedure in which a balloon-tipped catheter, a long thin, hollow plastic tube, is guided into an artery and advanced to a blockage or narrowing in a blood vessel. The balloon is then inflated to open the vessel, deflated and removed.
- balloon assisted technique
- A technique that uses balloons to open narrowed blood vessels.
- barium (Ba)
- (ba-rE-um, bA-rE-um)
- A metallic, alkaline, divalent earth element; atomic no. 56, atomic wt. 137.327.
- barium sulfate
- A white insoluble radiopaque powder that is used as a contrast material to make certain body parts more visible in x-ray images. Radiopaque substances limit the penetration of x-rays and other forms of radiation.
- barium swallow
- Also called an esophagram. An x-ray examination that assesses both the pharynx and esophagus in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- baseline
- Initial.
- becquerel (Bq)
- (bek-rel)
- The SI unit of measurement of radioactivity, equal to 1 disintegration per second;;
1 Bq = 0.027 × 10-9 Ci.
- benign
- (bE-nIn)
- Not cancerous. May also be defined as non-malignant. Benign is also used to describe medical conditions that have a mild course.
- benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- An enlarged prostate gland common in older men. For more information, see the Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia page.
- beta blocker
- A type of medicine used to lower blood pressure, treat chest pain and heart failure, and to prevent a heart attack.
- beta-amyloid plaque
- Thick deposits of proteins in the brain considered one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
- Bexxar®
- An iodine-131 agent used in radioimmuniotherapy to treat non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- bile
- A greenish-yellow fluid secreted by the liver, stored in the gallbladder and released through tubular passageways called bile ducts into the bowel to help digest fat and carry away waste.
- bile ducts
- Tubular passageways in the liver that carry bile, a greenish-yellow fluid secreted by the liver, to aid in the digestion of fat and transport waste out of the liver.
- biliary atresia
- A condition present at birth in which there is a blockage in the ducts that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder.
- biliary system
- See biliary tract.
- biliary tract
- Also called the biliary system.
Includes the gallbladder and tubular structures called ducts that course through the liver. Bile, a greenish-yellow fluid secreted by the liver, is stored in the gallbladder and released into the bowel through bile ducts to help the small intestine digest fat and carry away waste.
- biologically active coils
- A type of coil, made of soft platinum wire smaller than a strand of hair and available in different diameters and lengths, used in a procedure called a detachable coil embolization to treat an aneurysm (a bulge) or a blood vessel malformation called a fistula (a false passageway) that occurs in the brain and other parts of the body. Using image guidance, the coils are placed at the site of a bulge or passageway, where it helps block the flow of blood and prevents a rupture of the vessel.
- biometrics
- Biometrics requires a user to provide a unique identifier, such as a fingerprint or voice sample, which is compared to a stored record before the user can gain access to the computer.
- biopsy
- (bI-op-sE)
- Process of removing tissue from living patients for diagnostic examination.
- A specimen obtained by biopsy.
See the Biopsies page for additional information.
- bladder
- A balloon-like organ where urine is stored before being passed from the body.
- bleeding disorder
- A condition in which the body's blood clotting mechanism, which turns blood from a free-flowing liquid to a thickened state, is defective.
- blood clot
- A thickened mass of blood. For additional information see the Blood Clots page.
- blood clotting
- See blood coagulation.
- blood coagulation
- Also called blood clotting.
A process in which blood changes from a free-flowing liquid to a semi-solid gel.
- blood oxygenation
- The level of oxygen in the blood.
- blood thinning agents
- Also known as blood thinners. Medicine used to prevent blood clots from forming or getting larger.
- bone marrow
- The soft tissue that fills the cavities of bones in which blood cells are produced.
- bore
- The center of the cylindrical shaped magnet (often referred to as a doughnut) within an magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner.
Click image to view larger
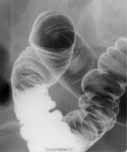
- bowel
- The part of the digestive system distal to the stomach, consisting of the small and large intestines, that digest and eliminate food.
- bowel cancer
- See colorectal cancer.
- brachytherapy
- (bray-key-therapy)
- Also called internal radiation therapy.
A type of radiation therapy used to treat cancer, involving the placement of a radioactive material, either temporarily or permanently, directly inside the body. For more information please refer to the Brachytherapy page.
- brain herniation
- An often fatal condition that results when brain tissue, fluid or blood vessels are pushed outside the skull.
- brain mapping
- Mapping the brain's surface using small electrodes to stimulate a nerve so its electrical response can be measured. By determining the role of specific nerves in a patient, this technique helps surgeons avoid damage to sensitive areas while operating on the brain.
- BRCA1 and BRCA 2
- Human genes that belong to a class of genes known as tumor suppressors. A mutation of these genes has been linked to hereditary breast and ovarian cancers.
- breast coil
- A wire coil placed around the breast that sends and receives radio waves within the magnetic field of an MRI unit to create images.
- bronchi
- The large air passages that lead from the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs.
- bronchial tubes
- Tubes that carry air from the windpipe into the lungs.
- bronchiectasis
- A dilation (widening) of the bronchi (the "breathing tubes"), often caused by infection. Serious complications may occur, and some patients require surgical removal of the affected part of the lungs.
- bronchitis
- (brong-kI-tis)
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the two subdivisions of the trachea (air tube) that conveys air to and from the lungs.
- bronchoscope
- An instrument for examination of the trachea and bronchi.
- bronchoscopy
- Visual inspection of the inside of the trachea and the bronchial passages of the lungs, using a rigid or flexible tube.
- bruit
- An abnormal sound heard when listening with a stethoscope over an organ or blood vessel such as the carotid artery in the neck.
- Budd-Chiari syndrome
- A blockage of one or more hepatic veins, which carry blood from the liver back toward the heart.
- bulla, pl. bullae
- A thin-walled air "cyst" within the lung, found in patients with emphysema.
- bursa, pl. bursae
- (bur-suh)
- A closed sac or envelope lined with a membrane and containing lubricating fluid, usually found or formed in areas subject to friction; e.g., over an exposed or prominent part or where a tendon passes over a bone.
|
|