Glossary of Terms
Enter
a term in the text box and press Find.
For a list of terms, select a letter or enter starting letter(s). |
|
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
M
N
O
P
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
[All]
|
|
|
- laceration
- A torn wound or cut.
- laparoscope
- A thin, tube-like instrument with an attached light and a lens for viewing the inside of the abdominal cavity.
- laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Gallbladder removal using small abdominal incisions and a laparoscope, a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing the inside of the abdominal cavity.
- laparoscopy
- Examination of a body cavity such as the pelvis using an illuminated tube that is inserted through a small incision.
- Examination of the lining of the abdominal wall with a laparoscope.
- laser
- A device emitting intense, focused light energy that can destroy tissues as an alternative to conventional surgical removal.
- lateral view
- (lat-er-al)
- On the side.
- laxative
- (lak-sa-tiv)
- Mildly cathartic; having the action of loosening the bowels.
- A mild cathartic; a remedy that moves the bowels slightly without pain or violent action.
- leiomyoma
- A benign tumor derived from smooth muscle. In the uterus, commonly called a fibroid.
- lesion
- An area of abnormal tissue on the skin or within the body caused by injury or disease. A lesion may be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
- lethal-ice
- Water frozen -40°C (-40°F) or less, which kills cells.
- leukemia
- Cancer of the blood cells that starts in the bone marrow, the soft tissue inside most bones.
- Lifeport
- Manufacturer's name. See implanted port.
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- A rare hereditary condition that increases a person’s risk of a wide range of tumors, including breast cancer and sarcomas of soft tissue.
- linear accelerator (LINAC)
- A device imparting high velocity and energy to atomic and subatomic particles; an important device for radiation therapy. See the Linear Accelerator page for more information.
- liquid nitrogen
- Nitrogen gas in a liquid state. The extreme cold of liquid nitrogen at -196°C is used in cryosurgery to freeze and destroy diseased tissue, including cancer cells.
- lithotripsy
- (lith-O-trip-sE)
- The crushing of a stone in the renal pelvis, ureter, or bladder, by mechanical force or sound waves.
Click image to view larger
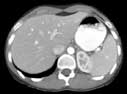
- liver
- (liv-er)
- The largest gland of the body, lying beneath the diaphragm; it is of irregular shape and weighs from 1 to 2 kg (2 to 4 pounds). It secretes the bile and is also of great importance in both carbohydrate and protein metabolism.
- lobules
- Glands that make breast milk.
- local anesthesia
- The use of medications called anesthetics to produce a temporary loss of sensation in a specific area of the body during a surgical or other medical procedure. While the local area affected by the anesthetic becomes numb, the patient remains awake and responsive.
- local anesthetic (“numbing agent”)
- A medication, also called a numbing agent, which produces a temporary loss of sensation in a specific area of the body during a surgical or other medical procedure. Local anesthesia may be administered as an injection under the skin or as a topical cream or patch applied to the surface of the skin in order to make the local area numb.
- localization
- (lO-kal-i-zA-shun)
- Limitation to a definite area.
- The reference of a sensation to its point of origin.
- The determination of the location of a morbid process.
- Low dose rate (LDR) brachytherapy
- A radiation therapy treatment for cancer that involves the placement of a radioactive material directly inside the body, in or near a tumor, for a specific amount of time and then withdrawn. In LDR brachytherapy, the patient is treated with a low dose of radiation for hours at a time.
- low-dose computed tomography (LDCT)
- Computed tomography (CT) scanning combines special x-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce multiple, cross-sectional images or pictures of the inside of the body. Low-dose CT or LDCT uses less ionizing radiation than a conventional CT scan.
- lumbar
- Refers to the low back region of the spinal column, which includes five bones, or vertebrae, labeled L-1 through L-5.
- lumbar puncture
- Also called spinal tap.
A minimally invasive diagnostic test that involves the removal of a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid—the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord—or an injection of medication or another substance into the lumbar (or lower) region of the spinal column.
- lumen, pl. lumina, lumens
- (lU-men, -min-a, -menz)
- The space in the interior of a tubular structure, such as an artery or the intestine.
- lumina
- (lU-min-a)
- See lumens.
- lumpectomy
- (lum-pek-tO-mE)
- The surgical removal of a small tumor (a lump). Lumpectomy generally refers to the removal of a lump from the breast as an alternative to mastectomy, which is the removal of the entire breast including the lump.
- lung
- One of a pair of organs of respiration in the chest in which aeration of the blood takes place. As a rule, the right lung is slightly larger than the left and is divided into three lobes (an upper, a middle, and a lower), while the left has but two lobes (an upper and a lower). Each lung is irregularly conical in shape, presenting a blunt upper extremity (the apex), a concave base following the curve of the diaphragm, an outer convex surface following the inner curve of the ribs, an inner or mediastinal surface, a thin and sharp anterior border, and a thick and rounded posterior border.
- lung volume reduction surgery
- The removal of part of the damaged lung, which creates additional space for the remaining healthy lung tissue to expand more easily. This surgery is only used for those with severe emphysema.
- lymph
- (limf)
- A clear, transparent, sometimes faintly yellow and slightly opalescent fluid that is collected from the tissues throughout the body, flows in the lymphatic vessels (through the lymph nodes), and is eventually added to the venous blood circulation. Lymph consists of a clear liquid portion, varying numbers of white blood cells (chiefly lymphocytes), and a few red blood cells.
- lymph node biopsy
- The removal of all or part of a lymph node to be examined under a microscope by a pathologist (a physician specializing in the examination of cells and tissues) to see if cancer cells are present.
- lymph nodes
- Small structures throughout the body that filter lymph fluid and collect inflammatory cells, keeping them from spreading infection.
- lymphangiography
- A diagnostic x-ray procedure that requires surgical incisions and injections directly into the lymphatic system. This procedure has been replaced by lymphoscintigraphy.
- lymphatic system
- A network of small channels similar to blood vessels that circulate fluid (called lymph) and cells (lymphocytes) of the immune system throughout the body.
- lymphedema
- A condition in which tissue fluid does not drain normally through the lymphatic system, causing swelling, usually of a leg or arm.
- lymphocytes
- Cells of the immune system. The two major subgroups of lymphocytes are: B cells that produce antibodies and T cells that destroy pathogens.
- lymphoma
- A group of cancers that involve the cells of the immune system, called lymphocytes. There are two major categories of lymphoma: Hodgkin (HL) and non-Hodgkin (NHL).
- lymphoscintigraphy
- (LIM-fo-sin-TIG-rah-fee)
- A special type of noninvasive nuclear medicine imaging that provides pictures called scintigrams of the lymphatic system. See the Lymphoscintigraphy page for more information.
|
|