Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Prostate
- What is MRI of the Prostate?
- What are some common uses of the procedure?
- How should I prepare?
- What does the equipment look like?
- How does the procedure work?
- How is the procedure performed?
- What will I experience during and after the procedure?
- Who interprets the results and how do I get them?
- What are the benefits vs. risks?
- What are the limitations of MRI of the Prostate?
What is MRI of the Prostate?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions.
MRI uses a powerful magnetic field, radio frequency pulses and a computer to produce detailed pictures of organs, soft tissues, bone and virtually all other internal body structures. The images can then be examined on a computer monitor, transmitted electronically, printed or copied to a CD. MRI does not use ionizing radiation (x-rays).
Detailed MR images allow physicians to evaluate various parts of the body and determine the presence of certain diseases.
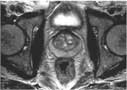
The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system. It is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder, where urine is stored, and surrounds the first part of the urethra, the tube that connects the bladder with the tip of the penis and carries urine and other fluids out of the body. The prostate helps make the milky fluid called semen that carries sperm out of the body when a man ejaculates. Ultrasound and MRI are the most commonly used techniques to image the prostate gland. See the Prostate Ultrasound page (www.RadiologyInfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=us-prostate) for more information.
What are some common uses of the procedure?
The primary indication for MRI of the prostate is the evaluation of prostate cancer. The test is commonly used to evaluate the extent of prostate cancer in order to determine if the cancer is confined to the prostate, or if it has spread outside of the prostate gland.
Occasionally, MRI of the prostate is used to evaluate other prostate problems, including:
- infection (prostatitis) or prostate abscess.
- an enlarged prostate, called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
- congenital abnormalities.
- complications after pelvic surgery.
How should I prepare?
Your MRI exam may, but will not necessarily involve the use of an endorectal coil, a thin wire covered with a latex balloon, placed inside the tail end of the large bowel, called the rectum. The rectum is located inside the pelvis immediately behind and up against the prostate gland. Placing this coil into the rectum so close to the prostate helps generate more detailed images from the prostate and surrounding structures; it also enables your radiologist to perform magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy, which can provide additional information on the chemical makeup of cells present in the prostate gland. Additionally, prostate MRI may examine water molecules motion (called water diffusion) and blood flow (called perfusion imaging) within the prostate to help differentiate abnormal (diseased) from normal prostate tissue.
You may be asked to wear a gown during the exam or you may be allowed to wear your own clothing if it is loose-fitting and has no metal fasteners.
Guidelines about eating and drinking before an MRI exam vary with the specific exam and also with the facility. Unless you are told otherwise, you may follow your regular daily routine and take food and medications as usual.
Some MRI examinations may require the patient to receive an injection of contrast material into the bloodstream. The radiologist, technologist or a nurse may ask if you have allergies of any kind, such as an allergy to iodine or x-ray contrast material, drugs, food, or the environment, or if you have asthma. The contrast material most commonly used for an MRI exam contains a metal called gadolinium. Gadolinium can be used in patients with iodine contrast allergy, after appropriate pre-medication (this will depend on local policies of the imaging facility). Patient consent may be requested in this instance. For more information on adverse reactions to gadolinium-based contrast agents, please consult the ACR Manual on Contrast Media. (http://www.acr.org/Quality-Safety/Resources/Contrast-Manual)
The radiologist should also know if you have any serious health problems, or if you have recently had surgery. Some conditions, such as severe kidney disease may prevent you from being given contrast material for an MRI. If there is a history of kidney disease or liver transplant, it may be necessary to perform a blood test to determine whether the kidneys are functioning adequately.
If you are not allergic to latex, you may receive an endorectal MRI, otherwise you need to let the MR technologist know so that they may cover the endorectal coil with a latex-free condom. To prepare for an MRI with the endorectal coil, you should eat light meals on the day prior to and on the day of your exam. This will help make it easier to insert the coil. You may also be asked to use an enema preparation prior to your exam. An enema involves injecting liquid into your rectum through your anus to help clear the bowel. Enema kits or saline laxatives can be bought over-the-counter. Prior to your exam, you may continue to take your usual medications, unless you are told otherwise.
If you have claustrophobia (fear of enclosed spaces) or anxiety, you may want to ask your physician for a prescription for a mild sedative prior to the scheduled examination.
Jewelry and other accessories should be left at home if possible, or removed prior to the MRI scan. Because they can interfere with the magnetic field of the MRI unit, metal and electronic objects are not allowed in the exam room. These items include:
- jewelry, watches, credit cards and hearing aids, all of which can be damaged
- pins, hairpins, metal zippers and similar metallic items, which can distort MRI images
- removable dental work
- pens, pocket knives and eyeglasses
- body piercings
In most cases, an MRI exam is safe for patients with metal implants, except for a few types. People with the following implants cannot be scanned and should not enter the MRI scanning area unless explicitly instructed to do so by a radiologist or technologist who is aware of the presence of any of the following:
- cochlear (ear) implant
- some types of clips used on brain aneurysms
- some types of metal coils placed within blood vessels
You should tell the technologist if you have medical or electronic devices in your body, because they may interfere with the exam or potentially pose a risk, depending on their nature and the strength of the MRI magnet. Some implanted devices require a short period of time after placement (usually six weeks) before being safe for MRI examinations. Examples include but are not limited to:
- artificial heart valves
- implanted drug infusion ports
- implanted electronic device, including a cardiac defibrillator, pacemaker or retained leads.
- artificial limbs or metallic joint prostheses
- implanted nerve stimulators
- metal pins, screws, plates, stents or surgical staples
In general, metal objects used in orthopedic surgery pose no risk during MRI. However, a recently placed artificial joint may require the use of another imaging procedure. If there is any question of their presence, an x-ray may be taken to detect and identify any metal objects.
Patients who might have metal objects in certain parts of their bodies may also require an x-ray prior to an MRI. You should notify the technologist or radiologist of any shrapnel, bullets, or other pieces of metal which may be present in your body due to accidents. Foreign bodies near the eyes are particularly important. Dyes used in tattoos may contain iron and could heat up during MRI, but this is rarely a problem. Tooth fillings and braces usually are not affected by the magnetic field, but they may distort images of the facial area or brain, so the radiologist should be aware of them.
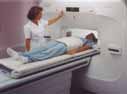
What does the equipment look like?
The traditional MRI unit is a large cylinder-shaped tube surrounded by a circular magnet. You will lie on a moveable examination table that slides into the center of the magnet.
Some MRI units, called short-bore systems, are designed so that the magnet does not completely surround you; others are open on the sides (open MRI). These units are especially helpful for examining patients who are fearful of being in a closed space and for those who are very obese. Newer open MRI units provide very high quality images for many types of exams; however, open MRI units with older magnets may not provide this same image quality. Certain types of exams cannot be performed using open MRI. For more information, consult your radiologist.
The computer workstation that processes the imaging information is located in a separate room from the scanner.
How does the procedure work?
Unlike conventional x-ray examinations and computed tomography (CT) scans, MRI does not depend on ionizing radiation. Instead, while in the magnet, radio waves redirect the axes of spinning protons, which are the nuclei of hydrogen atoms.
The magnetic field is produced by passing an electric current through wire coils in most MRI units. Other coils, located in the machine and in some cases, placed around the part of the body being imaged, send and receive radio waves, producing signals that are detected by the coils.
A computer then processes the signals and generates a series of images, each of which shows a thin slice of the body. The images can then be studied from different angles by the interpreting radiologist.
Frequently, the differentiation of abnormal (diseased) tissue from normal tissues is better with MRI than with other imaging modalities such as x-ray, CT and ultrasound.
How is the procedure performed?
MRI examinations may be performed on outpatients or inpatients.
You will be positioned on the moveable examination table. Straps and bolsters may be used to help you stay still and maintain the correct position during imaging.
Devices that contain coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves may be placed around or adjacent to the area of the body being studied.
If an endorectal coil is to be used during the exam, a nurse or physician will place a disposable cover over the coil, lubricate the assembly and insert the coil into your rectum. Once inserted, a circular balloon is inflated which sits around the coil and holds it in place during the exam. When the exam is complete, the balloon is deflated and the coil is removed.
If a contrast material will be used in the MRI exam, a physician, nurse or technologist will insert an intravenous (IV) catheter, also known as an IV line, into a vein in your hand or arm. A saline solution may be used. The solution will drip through the IV to prevent blockage of the IV catheter until the contrast material is injected.
You will be moved into the magnet of the MRI unit and the radiologist and technologist will leave the room while the MRI examination is performed.
If a contrast material is used during the examination, it will be injected into the intravenous line (IV) after an initial series of scans. Additional series of images will be taken during or following the injection.
When the examination is completed, you may be asked to wait until the technologist or radiologist checks the images in case additional images are needed.
Your intravenous line will be removed.
MRI exams generally include multiple runs (sequences), some of which may last several minutes.
The entire examination is usually completed within 45 minutes or less.
MR spectroscopy, which provides additional information on the chemicals present in the body's cells, may also be performed during the MRI exam and may add approximately 15 minutes to the total exam time.
What will I experience during and after the procedure?
Most MRI exams are painless. However, some patients find it uncomfortable to remain still during MR imaging. Others experience a sense of being closed-in (claustrophobia). Therefore, sedation can be arranged for those patients who anticipate anxiety, but fewer than one in 20 require medication.
During insertion of the endorectal coil you may feel pressure in your rectum similar to that experienced during a digital rectal exam.
It is normal for the area of your body being imaged to feel slightly warm, but if it bothers you, notify the radiologist or technologist. It is important that you remain perfectly still while the images are being recorded, which is typically only a few seconds to a few minutes at a time. For some types of exams, you may be asked to hold your breath. You will know when images are being recorded because you will hear tapping or thumping sounds when the coils that generate the radiofrequency pulses are activated. You will be able to relax between imaging sequences, but will be asked to maintain your position as much as possible.
You will usually be alone in the exam room during the MRI procedure. However, the technologist will be able to see, hear and speak with you at all times using a two-way intercom. Many MRI centers allow a friend or parent to stay in the room as long as they are also screened for safety in the magnetic environment.
You may be offered or you may request earplugs to reduce the noise of the MRI scanner, which produces loud thumping and humming noises during imaging. Children will be given appropriately sized earplugs or headphones during the exam. MRI scanners are air-conditioned and well-lit. Some scanners have music to help you pass the time.
When the contrast material is injected, it is normal to feel coolness and a flushing sensation for a minute or two. The intravenous needle may cause you some discomfort when it is inserted and once it is removed, you may experience some bruising. There is also a very small chance of irritation of your skin at the site of the IV tube insertion.
If you have not been sedated, no recovery period is necessary. You may resume your usual activities and normal diet immediately after the exam. A few patients experience side effects from the contrast material, including nausea and local pain. Very rarely, patients are allergic to the contrast material and experience hives, itchy eyes or other reactions. If you experience allergic symptoms, a radiologist or other physician will be available for immediate assistance.
Who interprets the results and how do I get them?
A radiologist, a physician specifically trained to supervise and interpret radiology examinations, will analyze the images and send a signed report to your primary care or referring physician, who will share the results with you.
Follow-up examinations may be necessary, and your doctor will explain the exact reason why another exam is requested. Sometimes a follow-up exam is done because a suspicious or questionable finding needs clarification with additional views or a special imaging technique. A follow-up examination may also be necessary so that any change in a known abnormality can be monitored over time. Follow-up examinations are sometimes the best way to see if treatment is working or if an abnormality is stable over time.
What are the benefits vs. risks?
Benefits
- MRI is a noninvasive imaging technique that does not involve exposure to ionizing radiation.
- MR images of the soft-tissue structures of the body including the prostate and other pelvic structures are clearer and more detailed than with other imaging methods. This detail makes MRI a valuable tool in early diagnosis and evaluation of the extent of tumors, such as prostate cancer.
- MRI has proven valuable in diagnosing a broad range of conditions, including cancer, and benign conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia and infection.
- MR spectroscopy can examine the chemical makeup of the prostate which can be helpful in identifying prostate cancer. MR diffusion and MR perfusion imaging can evaluate other tissue properties of normal prostate tissue and prostate cancer.
- MRI enables the discovery of abnormalities that might be obscured by bone with other imaging methods.
- The contrast material used in MRI exams is less likely to produce an allergic reaction than the iodine-based contrast materials used for conventional x-rays and CT scanning.
Risks
- The MRI examination poses almost no risk to the average patient when appropriate safety guidelines are followed.
- If sedation is used, there are risks of excessive sedation. The technologist or nurse monitors your vital signs to minimize this risk.
- Although the strong magnetic field is not harmful in itself, implanted medical devices that contain metal may malfunction or cause problems during an MRI exam.
- There is a very slight risk of an allergic reaction if contrast material is injected. Such reactions usually are mild and easily controlled by medication. If you experience allergic symptoms, a radiologist or other physician will be available for immediate assistance.
- Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is currently a recognized, but rare, complication of MRI believed to be caused by the injection of high doses of gadolinium-based contrast material in patients with very poor kidney function. Careful assessment of kidney function before considering a contrast injection minimizes the risk of this very rare complication.
What are the limitations of MRI of the Prostate?
High-quality images are assured only if you are able to remain perfectly still while the images are being recorded. If you are anxious, confused or in severe pain, you may find it difficult to lie still during imaging.
A person who is very large may not fit into the opening of certain types of MRI machines.
The presence of an implant or other metallic object sometimes makes it difficult to obtain clear images. Patient movement can have the same effect.
MRI cannot always distinguish between cancer tissue and inflammation or presence of blood products within the prostate, which sometimes occurs related to a prostate biopsy. To avoid confusing the latter with the former on imaging, prostate MRI may be performed six to eight weeks after prostate biopsy, if possible, to allow remnants of bleeding to resolve.
MRI typically costs more and may take more time to perform than other imaging modalities.
Additional Information and Resources
RadiologyInfo
Prostate Cancer:
(www.RadiologyInfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=pros_cancer)
RTAnswers.org
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer:
(www.rtanswers.com/treatmentinformation/cancertypes/prostate/index.aspx)
Locate an ACR-accredited provider: To locate a medical imaging or radiation oncology provider in your community, you can search the ACR-accredited facilities database.
This website does not provide costs for exams. The costs for specific medical imaging tests and treatments vary widely across geographic regions. Many—but not all—imaging procedures are covered by insurance. Discuss the fees associated with your medical imaging procedure with your doctor and/or the medical facility staff to get a better understanding of the portions covered by insurance and the possible charges that you will incur.
Web page review process: This Web page is reviewed regularly by a physician with expertise in the medical area presented and is further reviewed by committees from the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), comprising physicians with expertise in several radiologic areas.
Outside links: For the convenience of our users, RadiologyInfo.org provides links to relevant websites. RadiologyInfo.org, ACR and RSNA are not responsible for the content contained on the web pages found at these links.
Images: Images are shown for illustrative purposes. Do not attempt to draw conclusions or make diagnoses by comparing these images to other medical images, particularly your own. Only qualified physicians should interpret images; the radiologist is the physician expert trained in medical imaging.
This page was reviewed on May 09, 2013