Patient Safety:
What are the benefits of CT scans?
Computed tomography (CT or CAT scan) ranks as one of the top five medical developments in the last 40 years, according to most medical surveys. CT has proven so valuable as a medical diagnostic tool that the 1979 Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded to the inventors.
How it works
Both CT and conventional x-rays take pictures of internal body structures. In conventional x-rays, the structures overlap. For example, the ribs overlay the lung and heart. In an x-ray, structures of medical concern are often obscured by other organs or bones, making diagnosis difficult.
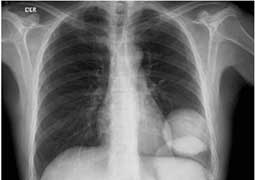
X-ray image showing internal body structures
In a CT image, overlapping structures are eliminated, making the internal anatomy more apparent.
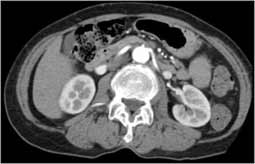
CT image showing internal body structures
During CT imaging, an x-ray tube rotates around the patient so that multiple images are collected from many angles. These images are stored in a computer that analyzes them to create a new image with the overlying structures removed.
CT images allow radiologists and other physicians to identify internal structures and see their shape, size, density and texture. This detailed information can be used to determine if there is a medical problem as well as the extent and exact location of the problem, and other important details. The images can also show if no abnormality is present.

A CT scan that shows no abnormality still provides useful data. The information aids a diagnostician by focusing attention away from unnecessary medical concerns.
Modern CT scanners acquire this information in seconds – sometimes in fractions of a second – depending on the examination.
Benefits
Benefits of CT include more effective medical management by:
- determining when surgeries are necessary
- reducing the need for exploratory surgeries
- improving cancer diagnosis and treatment
- reducing the length of hospitalizations
- guiding treatment of common conditions such as injury, cardiac disease and stroke
- improving patient placement into appropriate areas of care, such as intensive care units
In an emergency room, patients can be scanned quickly so doctors can rapidly assess their condition. Emergency surgery might be necessary to stop internal bleeding. CT images show the surgeons exactly where to operate. Without this information, the success of surgery is greatly compromised. The risk of radiation exposure from CT is very small compared to the benefits of a well-planned surgery.
CT scanning provides medical information that is different from other imaging examinations, such as ultrasound, MRI, SPECT, PET or nuclear medicine. Each imaging technique has advantages and limitations. The principal advantages of CT are:
- Rapid acquisition of images
- A wealth of clear and specific information
- A view of a large portion of the body
No other imaging procedure combines these advantages into a single session.
This page was reviewed on August 19, 2011


